TDG
- TDG Home
- TDG Directorate
- Emergency Response Task Force
- CANUTEC
- TDG Act
- TDG Regulations
- Protective Directions
- Interim Orders
- Consultation
- Containers
- Equivalency Certificates (Permits)
- Emergency Response Assistance Plans
- Safety Awareness Materials and FAQ
- TDG Publications
- Enforcement Actions Summaries
- TDG Security
- Training
- Contraventions
- TDG Contact Us / Contacts
- Links
- TDG Site Map
Coming into force on:
Changes brought forward by Amendment no. 6 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations came into force on February 20, 2008.
Changes:
Changes from Amendment no. 6 will affect numerous parts of the Regulations. Below, is a list of the parts that were modified. To consult these changes, follow the link to each Part by clicking on the Part you would like to consult. The text that follows does not replace the Regulations, safety standards or safety requirements that apply. For interpretation and application, you should consult the Canada Gazette, Part II and other official regulatory documents. It is important to note that Amendment No.6 came into effect after Amendment No. 7. Therefore, you must consult Canada Gazette, Part II and refer to registration SOR/2008-34 to find the modifications summarized below.
- Part 1 Coming into Force, Repeal, Interpretation, General Provisions
and Special Cases. - Part 2 Classification
- Part 3 Documentation
- Part 4 Dangerous Goods Safety Marks
- Part 5 Means of Containment
- Part 7 Emergency Response Assistance Plan (ERAP)
- Part 8 Accidental Release and Eminent Accidental Release Report
Requirements - Part 9 Road
- Part 10 Rail
- Part 11 Marine
- Part 12 Air
- Part 16 Inspectors
- Schedule 1 Classes 1 to 9
- Schedule 2 Special Provisions
- Schedule 3 Alphabetical Index
Part 1 — Coming into Force, Repeal, Interpretation, General Provisions and Special Cases.
Changes in this part relate to the following three sections; 1) Interpretation, including the table which makes references to the safety standards or safety requirements and definitions that applies to the Regulations, 2) General provisions and finally, 3) Special cases. Below, you will find a brief summary of these changes:
Interpretation
1.3(2)(b) The term ‘Aircraft' was added to this subparagraph.
1.3(2)(d) Subparagraph (iv) was added, it now states that in a shipping name for solutions or mixtures, followed by the word ‘SOLUTION' or ‘MIXTURE', as appropriate, and may include the concentration of the solution or mixture.
1.3(2)(f) Paragraph (f) was added it specifies that when the word ‘placard' is used, it refers to a specific placard illustrated in the Appendix 4 to Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, but when a placard is required to be displayed, the singular includes the plural and it means the appropriate number of placards as required by Part 4.
1.3(2)(g) A paragraph was added to define the meaning of the term ‘or'.
1.3(2)(h) Document:
Paragraph (h) was added to specify that when referring to a shipping document or a required document, the requirements include either the original or a copy of the shipping document or the original document.
1.3(2)(i) Explosives:
Paragraph (i) was added to stipulate that when converting between the number of articles and the net explosives quantity, one kilogram of net explosives quantity must be counted as 100 articles and each 100 articles must be counted as one kilogram net explosives quantity.
1.3(2)(j) Minimum Means of Containment:
This paragraph was added to define what is the minimum required means of containment in order to determine which of the means of containment must be standardized.
It is also useful to:
- Determine the gross mass. See the definition of “gross mass” which is relevant in sections 1.6, 1.15, 1.16, 1.17, 1.19.1, 1.19.2, 1.20 and 7.1; and
- Clarify situations when dangerous goods safety marks do not need to be displayed on a means of containment inside the minimum required means of containment.
1.3(2)(k) Minimum Means of Containment:
This new paragraph states that when the words “means of containment” are used, they refer to the minimum means of containment, unless otherwise indicated.
1.3(2)(l) Gross Mass of All Dangerous Goods:
This new paragraph states that the words “gross mass of all dangerous goods” in sections 1.15, 1.16, 1.21 and 1.22 refer to dangerous goods that require shipping documents or that are intended to be transported in accordance with those sections.
1.3.1 Table of references:
The Table of Safety Standards and Safety Requirement Documents has been moved from 1.3(f) to 1.3.1. This table has been updated to reflect the most recent versions of the documents. The following referenced documents' versions were changed:
- 49 CFR
- CGA P-20
- CGSB-43.147
- CSA B339
- CSA B620
- CSA B621
- CSA B622
- ICAO Technical Instructions
- Manual of Tests and Criteria
- IMDG
- Supplement to the ICAO Technical Instructions
- ULC – S504
- ULC – S507
- ULC – S512
- ULC – S554
1.4 Definitions:
This section was modified by the removal, replacement or addition of some definitions. The changes are as follows:
Three definitions were removed:
- diagnostic specimen
- risk group
- water capacity
The following definitions have changed:
- Biological product
- 49 CFR
- classification
- consignment
- gross mass
- ICAO Technical Instructions
- IMDG Code
- infectious substance
- large means of containment
- Manual of Tests and Criteria
- net explosives quantity
- person
- road vehicle
- small means of containment
- Supplement to the ICAO Technical Instructions
- UN Recommendations
The following definitions were added:
- Capacity
- Category A
- Category B
- Culture
- Drum
- Farmer
- Farming
- Type 1A means of containment
- Type 1B means of containment
- Type 1C means of containment
General Provisions:
1.5 Applicability of the Regulations:
This section replaces sections 1.5 and 1.6. It now specifies that unless otherwise stated in sections 1.15 to 1.48 of this Part or in Schedule 1, Classes 1 to 9 and Schedule 2, Special Provisions, dangerous goods must be handled, offered for transport or transported in accordance with these Regulations.
1.5.1 Schedule 2: Special Provisions
This text was previously in 1.5(3) and 1.5(4). This new section specifies that when there is a conflict between a special provision and other provisions within the Regulations, the special provision applies.
1.5.2 Schedules 1 and 3: Forbidden Dangerous Goods
This text was previously in 1.5(1) and 1.5(2). This new section defines the word “Forbidden” when shown in column 3 of Schedule 1, Classes 1 to 9, or column 4 of Schedule 3, Alphabetical Index, as well and when it is shown in column 8 or 9 of Schedule 1.
1.6 Schedule 1: Quantity Limits in Columns 8 and 9
This section was modified to better reflect the requirements particular to columns 8 and 9. The requirements for Column 8, Passenger Carrying Ship Index, are now found in subsection 1.6(1) and the requirements for Column 9, Passenger Carrying Road Vehicle or Passenger Carrying Railway Vehicle Index, are now found in subsection 1.6(2).
Special cases:
One of the major changes in this part is the removal of almost all of the expressions “These Regulations do not apply to…” This expression is replaced with different wording that indicates which parts do not apply. Consequently, Part 2, Classification, and the Schedules aren't automatically exempted. The dangerous goods will have to be classified before being transported or, indeed, in some cases before a consignor can determine if an exemption or the Schedules apply.
The sections that follow have been changed, replaced or added to Part 1, Coming into Forece, Repeal, Interpretation, General Provisions and Special Cases of the Regulations. This better reflects today's reality in the areas of handling, offering for transport, transporting and importing dangerous goods.
1.15 150 kg Gross Mass Exemption:
The title has been changed and this exemption is no longer restricted to personal use. If all conditions are met, anyone transporting dangerous goods can use this exemption. In fact, many services vehicles or other vehicles transporting small amounts of dangerous goods may choose to use this exemption. The gross mass permitted by this exemption remains at 150kg.
Other changes have also been made to this section, in particular, for dangerous goods included in Class 2, Gases, if they are in one or more small means of containment they must be in compliance with the requirements for transporting gases in Part 5, Means of Containment. Other requirements within this section have been added or modified. It is important to be aware of these changes before using this exemption.
1.16 500 kg Gross Mass Exemption:
One of the changes to this section includes stating which Parts of the Regulations the exemption applies to.
Hereafter, dangerous goods, other than those included in Class 2, Gases, can be transported in drums as per section 5.12 of Part 5, Means of Containment, in a quantity greater than 30kg.
Furthermore, as of now, the gross mass of all dangerous goods transported on a road or railway vehicle must be less than or equal to 500kg and transported on the ship on a domestic voyage is less than or equal to 500kg excluding the dangerous goods in a road or railway vehicle being transport on the ship.
Other requirements within this section have been added or modified. It is important to be aware of these changes before using this exemption.
1.17 Limited Quantities Exemption:
This section has been rewritten to better define a limited quantity. The term “consignment” is replaced by “A quantity of dangerous goods”. Furthermore, this section is now a partial exemption. Parts 3 to 8 do not apply.
As of now, a new requirement has been added in regards to the markings of the inner means of containment. The inner means of containment is not required to be marked, if the outer means of containment is not intended to be opened during transport.
It is now permitted to display the UN numbers of each of the limited quantities of dangerous goods preceded by the letters “UN” placed within a diamond-shaped mark to identify limited quantities of dangerous goods. The specific requirements can be found in sub-section 4.
Finally, when the gross mass of an accumulation of limited quantities of dangerous goods by one consignor to one destination is greater than 500kg the reporting requirements in Part 8, Accidental Release and Imminent Accidental Release Report Requirements must be complied with despite the exemption stated in subsection (2) of this section.
1.18a)(iii) Medical Device or Article:
This subparagraph has been repealed. Henceforth, there are no longer restrictions in terms of the capacity of the medical cylinder.
1.19 Section 1.19 has been divided into three sections.
1.19 Samples for Inspections or Investigation Exemption:
This section stipulates the requirements for samples for the purposes of inspection or investigation. This exemption states that the regulations do not apply to samples of goods, including forensic samples, that are reasonably believed to be dangerous goods if, for the purposes of inspection or investigation duties under an Act of Parliament or provincial legislature and the conditions of this section are met.
1.19.1 Samples Classifying, Analysing or Testing Exemption:
This section is an exemption used for samples taken for the purposes of classification, analysis or testing. If all conditions of this exemption are met, Parts 2 to 7 do not apply to samples of goods that the consignor reasonably believes to be dangerous goods but the classification or the exact chemical composition of the goods is unknown and cannot be readily determined if the conditions of this section are not met.
1.19.2 Samples Demonstration Exemption:
This section applies to samples being transported for demonstration purposes. Part 3, Documentation and Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks do not apply to samples being transported for demonstration purposes when they are transported in accordance with the requirements of this section.
1.21 Agriculture: 1500 kg Farm Vehicle Exemption:
This exemption has been replaced and now states that the gross mass of the dangerous goods must be less than or equal to 1500 kg on board a vehicle licensed as a farm vehicle. The exemption now applies only to Part 2 to 6. Other changes include:
- Class 2, Gases, must be in a means of containment that complies with Part 5, Means of Containment.
- Dangerous goods other than those included in Class 2, Gases, must be transported in a means of containment that is designed, constructed, filled, closed, secured and maintained so that under normal conditions of transport, including handling, there will be no accidental release of the dangerous goods that could endanger public safety.
- The dangerous goods are to be or have been used by a farmer for farming purposes.
Also, when an Emergency Response Assistance Plan (ERAP) is required, under Part 7, Emergency Response Assistance Plan, the dangerous goods that require an ERAP must be accompanied by a shipping document.
1.22 Agriculture: 3000 kg Gross Mass Retail Exemption:
This section has been replaced and now states that the exemption applies only that Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Safety Marks, and Part 5, Means of Containment. Other changes include:
- Class 2, Gases, must be in a means of containment that complies with Part 5, Means of Containment.
- Dangerous goods other than those included in Class 2, must be transported in a means of containment that is designed, constructed, filled, closed, secured and maintained so that under normal conditions of transport, including handling, there will be no accidental release of the dangerous goods that could endanger public safety.
- The dangerous goods are to be or have been used by a farmer for farming purposes.
Also, when an ERAP is required, under Part 7, Emergency Response Assistance Plan, the dangerous good that require an ERAP must be accompanied by a shipping document.
1.24 Agriculture: Anhydrous Ammonia Exemption:
The term “water capacity” has been replace with “capacity”.
1.26 Emergency Response Exemption:
The title of the exemption has been changed and the wording was changed to provide more detail on the scope of this section and to include requirements that were found in Part 12, Air.
1.27 Operation of a Means of Transport or a Means of Containment Exemption:
This exemption has been rewritten to clarify the different aspects of this section. It now makes the distinction between dangerous goods on a means of transport used for:
- The propulsion of the means of transport,
- The safety of individuals,
- The operation or safety of the means of transport (i.e. air bags, shock absorbers, fire extinguishers), or
- Ventilation, refrigeration or heating units that are necessary to maintain the environmental conditions within a means of containment in transport on the means of transport.
It is important to note this exemption does not apply to ammunition or dangerous goods being delivered to a destination and from which a portion is drawn off during transport for propulsion of the means of transport.
1.28 Transportation between two properties:
This section was modified to include the producers of dangerous goods. Now, manufacturers, producers and users must ensure that the means of transport must now have displayed on it:
- The placard for the primary class of each of the dangerous goods, or
- The DANGER placard.
Paragraph (c) of subsection (3) has been modified to state that in accordance with this section the dangerous goods may be transported in one or more means of containment.
Furthermore, the table in paragraph (d) has been removed and has been replaced with the following wording: “the local police are advised, in writing, of the nature of the dangerous goods no more than 12 months in advance of the transport”.
1.29 Dangerous goods in an Instrument or in Equipment:
This section has been replaced and now states that Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks and Part 5, Means of Containment do not apply to dangerous goods contained in, and are not intended to be discharged from an instrument or equipment that is not dangerous goods itself.
In the case of explosives, a paragraph has been added to specify what net explosives quantity is permitted to be transported when using this exemption. As well, two new special provisions that state the permitted quantity of articles that can be transported using this exemption have also been added.
1.30 Marine: Short-run Ferry Exemption:
Only the title of this section was changed.
1.31 Class 1, Explosives Exemption:
This section has been replaced and now states that Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, Part 6, Training, Part 9, Road, and Part 10, Rail, do not apply to the transport of some explosives under new conditions.
The way to determine if the net explosives quantity is less than or equal to the quantity indicated in column 6 of Schedule 1, Classes 1 to 9, has changed. Now, special provisions 85 and 86, Schedule 2, Special Provisions, must be taken into account when determining if this exemption can be applied to the explosives being transported.
Furthermore, paragraph (d) now specifies, that in certain circumstances a placard must be displayed in accordance with paragraph 4.15(1)(e) of Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks.
1.32 Class 2, Gases, in Refrigerating Machines Exemption:
This section has been replaced and now states that certain Class 2, Gases contained in refrigerating machines are exempted from Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, Part 5, Means of Containment, Part 6, Training, Part 7, Emergency Response Assistance Plan, Part 8, Accidental Release and Imminent Accidental Release Report Requirements, Part 9, Road and Part 10, Rail.
This exemption is specific to the following dangerous goods:
- REFRIGERATING MACHINES, UN2857
- Refrigerating machine components, containing class 2.2, Non-flammable, Non-toxic gases, or
- AMMONIA SOLUTIONS if the quantity of gas has a mass that is less than or equal to 12kg and the quantity of ammonia solutions is than or equal to 12L, UN2672.
1.32.1 Class 2, Gases, That May Be Identified as LIQUEFIED PETROLEUM GAS, UN1075:
This is a new section that replaces special provision 29 of Schedule 2, Special Provisions, in regards to LIQUEFIED PETROLEUM GAS, UN 1075.
This section applies to the same six liquefied petroleum gases however two new requirements have been added:
- The shipping name of the dangerous goods shipping name of the dangerous goods subject to this exemption may be shown on the shipping document following the words LIQUEFIED PETROLEUM GAS.
- If either, PROPYLENE, UN1077 or PROPANE, UN1978, is to be transported on a road or railway vehicle on board a ship and is identified as LIQUEFIED PETROLEUM GAS on the shipping document in accordance with subsection (1), the shipping name PROPYLENE or PROPANE, as appropriate, must be shown on the shipping document, in parentheses, following the words LIQUEFIED PETROLEUM GAS.
1.32.2 Gases, Absolute Pressure between 101.3 kPa and 280 kPa:
This new section is an exemption that allows the transportation of certain gases that have an absolute pressure between 101.3 kPa and 280kPa as Class 2,2, Non-flammable, Non-toxic gas.
1.32.3 Class 2, Gases, in Small Means of Containment Exemption:
This new section replaces special provision 42 Schedule 2, Special Provisions and includes new requirements. This exemption now applies to Part 3, Documentation and Part 6, Training. It now means that the requirements of Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, must be complied with.
Two new dangerous goods have been added to the list of gases:
- CARBON DIOXIDE, UN1013
- NITROGEN COMPRESSED, UN1066.
1.33 Class 3, Flammable Liquids, General Exemption:
This section has been modified. The exemption no longer applies to all of the regulations. It now states that Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, Part 5, Means of Containment, Part 6, Training, Part 7, Emergency Response Assistance Plan, Part 9, Road and Part 10, Rail, do not apply to dangerous goods included in Class 3, Flammable Liquids and that are transported on a road or railway vehicle, or a ship on a domestic voyage.
Furthermore, the dangerous goods can now be transported in one or more small means of containment. The other requirements of the section have not changed.
1.34 Class 3, Flammable Liquids, Flash Point Greater Than 60°C but Less Than or Equal to 93°C:
This section has been modified to reflect the new flash point range for this exemption. It has been changed to 60°C to 93°C. This change reflects the new classification requirements for Class 3, Flammable liquids in Part 2, Classification.
1.34.1 GASOLINE, UN1203, to operate an Instrument or Equipment Exemption:
This new section provides an exemption for GASOLINE, UN1203 used to operate an instrument or equipment. Part 3 to Part 6 of the regulations do not apply to the handling, offering for transport or transporting of GASOLINE, UN1203, that is in transport on a road vehicle, a railway vehicle or a ship on a domestic voyage if the dangerous goods are in a fuel tank with a capacity less than or equal to 200L and permanently mounted to the machine operated by fuel from that tank.
1.35 DIESEL FUEL, UN1202, or GASOLINE, UN1203, Exemption:
This exemption now applies only to dangerous goods transported on a road vehicle.
1.36 Class 3, Flammable Liquids, Alcoholic Beverage and Aqueous Solution of Alcohol Exemption:
This section has been replaced to incorporate new requirements. The exemption no longer applies to all of the regulations; it now applies only to Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, Part 5, Means of Containment, Part 6, Training, Part 7, Emergency Response Assistance Plan, Part 8, Accidental Release and Imminent Accidental Release Report Requirements, Part 9, Road and Part 10, Rail. The new requirements are specific to two types of alcoholic products:
- Alcoholic beverages
- Aqueous solution of alcohol
1.37 This exemption has been incorporated into section 1.36 b).
1.38 Polyester Resin Kit Exception:
The portion of the section before paragraph (a) is replaced. The exemption no longer applies to all of the regulations; it now applies only to Parts 3 to 10. Furthermore, this exemption can no longer be used for substances included in Class 5.2, type C. The rest of the requirements have not changed.
This section has replaced sections 1.39 and 1.40 since the term “risk group” has been removed.
1.39 Class 6.2, Infectious Substances, Category B Exemption:
This section introduces new requirements for dangerous goods included in Class 6.2, Infectious Substances in Category B.
Also it, exempts infectious substances included in Category B from Parts 3 to 7 when they are transported in accordance with the new means of containment and safety marks requirements of this section.
1.40 This section has been removed since the “risk groups” no longer exist.
1.41 Biological Products Exemption:
This section has been modified. The exemption now applies only to Parts 3 to 8. Also, it introduces a new requirement that states that the means of containment must be marked with the words "Biological Product" or "Produit biologique" in black letters at least 6 mm high on a contrasting background.
1.42 Human or Animal Specimens Believed Not to Contain Infectious Substances Exemption:
This section has been modified. It now includes new requirements for human or animal specimens that are not reasonably believed to contain infectious substances. The section has also been modified to reflect that the exemption now applies only to Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, Part 5, Means of Containment, Part 6, Training, Part 7, Emergency Response Assistance Plan, and Part 8, Accidental Release and Imminent Accidental Release Report Requirements.
1.42.1 Tissues or Organs for Transplant Exemption:
This new section states that these Regulations do not apply to the handling, offering for transport or transporting of tissues or organs for transplant.
1.42.2 Blood or Blood Components Exemption
This new exemption states that Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, Part 5, Means of Containment, Part 6, Training, Part 7, Emergency Response Assistance Plan, and Part 8, Accidental Release and Imminent Accidental Release Report Requirements, do not apply to the handling, offering for transport or transporting of blood or blood components that are intended for transfusion or for the preparation of blood products and are reasonably believed not to contain infectious substances. The blood or blood components must be in a means of containments that meets the requirements of this section,
1.43 Class 7, Radioactive Materials Exemption:
This section has been replaced to reflect that the exemption pertaining to Class 7, Radioactive Materials applies only to Part 3, Documentation, Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, Part 5, Means of Containment, Part 6, Training, Part 7, Emergency Response Assistance Plan, Part 9, Road, Part 10, Rail, Part 11, Marine, and Part 12, Air. The rest of the section has not been changed.
1.44 Dangerous Goods in a Drum Exemption:
This section was modified to change the order of the words. No other change has been added.
1.45.1 Marine Pollutants Exemption:
This new section states that Part 3, Documentation, and Part 4, Dangerous Goods Safety Marks, do not apply to substances that are classified as marine pollutants in accordance with section 2.43 of Part 2, Classification, if they are in transport solely on land by road vehicle or railway vehicle. However, substances may be identified as marine pollutants on a shipping document and the required dangerous goods safety marks may be displayed when they are in transport by road or railway vehicle.
1.46 Miscellaneous Special Cases:
Paragraph (m), sodium carbonate peroxyhydrate, is repealed.
1.47 FIRE EXTINGUISHERS, UN1044 Exemption:
This exemption replaces the previous section 1.47 regarding the handling or transporting of ammunition, or ammunition loaded in a firearm. The handling and transport can be done following the requirements of the new section 1.15 on board a road vehicle, roadway vehicle or a ship on a domestic voyage and in accordance with subsection (2) of section 12.4 of the TDG Regulations when transported on an aircraft.
This new section applies to FIRE EXTINGUISHERS, UN1044. Paragraphs 5.10(1)(a) and (b) and subsection 5.10(2) of Part 5, Means of Containment, do not apply to the handling, offering for transport or transporting of FIRE EXTINGUISHERS, UN1044, on a road vehicle, a railway vehicle or a ship on a domestic voyage if the fire extinguishers meet the requirements of this new section.
1.48 Air Ambulance Exemption:
This new section replaces the exemption that was repealed in section 12.15.
This is a new exemption for air ambulance. Except for Part 8, Accidental Release and Imminent Accidental Release Report Requirements, these regulations do not apply to dangerous goods required for patient care on an air ambulance when the requirements of this section are respected.
Part 2 — Classification
The changes made in this part of the Regulations concern mainly the way in which goods must be classified.
2.5.1 When goods are classified in accordance with sections 2.4 and 2.5, the description written in lower case letters following a shipping name must be used to determine the shipping name that most precisely describes the dangerous goods.
2.13a) Change in wording to better describe the way in which Class 2, Gases are classified.
2.18(1)a) Change in the maximum value of the flash point for the classification of flammable liquids, from 60.5oC to 60oC.
2.19(2)b) Change in the French wording arising from the new shipping name for UN1203. The French name is now ESSENCE.
2.28 Regarding the criteria for inclusion in Class 6.1, Toxic Substances, there is a change in the maximum values for inhalation toxicity and oral toxicity.
2.29 Regarding the determination of packing group, there is a change in the limiting values for oral, dermal and inhalation toxicity.
2.36 Section 2.36 is being replaced to remove the references to risk groups and add the concepts of Category A and Category B infectious substances of Class 6.2.
2.37 The approach to classifying Class 7, Radioactive Materials, is changed in order to harmonize the TDG Regulations with the Packaging and Transport of Nuclear Substances Regulations.
2.43 The classification requirements for Class 9, Miscellaneous Products, Substances or Organisms have been changed.
Appendix 2 The appendix describing Compatibility Groups, Class 1, Explosives, has been changed.
Appendix 3 This appendix replaces Appendixes 3 to 5 and incorporates the concept of Category A and Category B infectious substances. The appendix classifies these substances into one or the other of these two categories.
Part 3 — Documentation
The changes in Part 3, Documentation, mainly concern the way required information is recorded.
3.5 A new way of recording the subsidiary class or classes and the packing group is introduced, allowing them to be recorded under one “heading”. The requirement to indicate the risk group is eliminated, since it no longer exists.
It is now possible to use a unit of measure that is acceptable under the International System of Units to express the quantity of dangerous goods being transported. For example: 1 t = 1000 kg.
The required method of recording the number of small means of containment has been changed; the requirement now pertains to all classes.
3.5(6) This requirement has been removed since the transitional period is now over.
3.6(3) This subsection has been reworded.
3.9(2) This subsection has been reworded.
3.11(1)b) This subsection has been reworded.
3.11(3) This subsection has been reworded.
Part 4 — Dangerous Goods Safety Marks
Part 4 has been changed to make certain requirements clearer. Also, there are new requirements and safety marks.
4.4(1)b) Change of wording to make it clear that this requirement applies to each large means of containment that contains dangerous goods.
4.5 This section about carrier responsibilities has been changed. Gone is the option of leaving the DANGER placard displayed until the large means of containment no longer contains any of the dangerous goods that required the display of the placard. This option has been moved to section 4.9(2).
4.7(5) This subsection has been reworded.
4.8(2) A new requirement that spells out the colour and size of the UN number that must appear on a large means of containment (black, not less than 65 mm high).
4.9 The title of this section has been changed to “Removal or Change of Dangerous Goods Safety Marks”. Also, the person responsible for the means of containment is now responsible for changing or removing the safety marks. Subsection (2) now includes the option of leaving the DANGER placard displayed until the large means of containment no longer contains the dangerous goods for which the placard had been required. This provision used to be in section 4.5.
4.10(1)d) This change allows an interconnected combination of cylinders (each with a capacity greater than 225 L) to be placarded as one large means of containment. Certain other conditions apply.
4.11(1) The wording is changed to show that the shipping name must be displayed in cases where a primary class label must be displayed (rather than is displayed).
4.14 This section has been re-written to better describe the requirements concerning the display of the information that must appear on labels of dangerous goods of Class 7, Radioactive Materials.
4.15 A few changes have been made to better describe the requirements and to include the requirement of displaying a placard with certain explosives of Class 1. The section has also been changed to better describe the requirement to display a placard and a UN number on a large means of containment that are contained within another means of containment that require a placard.
The table in this section has also been changed. Items 3 and 4 of the table give new rules concerning the display of a DANGER placard.
4.17(1)a) This paragraph now states that AMMUNITION, TEAR-PRODUCING, UN0301, is not exempt from section 4.15.
4.18 The first three subsections have been re-written to clarify the existing requirements. The option remains of displaying placards when more than one primary class placard or more than one UN number are required by section 4.15, as do the requirements concerning road or railway vehicles transported on a ship and concerning the oxidizing gas placard for UN1072, UN1073, UN3156 and UN3157.
There are two new subparagraphs setting out the new requirements on, ANHYDROUS AMMONIA, UN1005. A new placard is added to the Appendix to Part 4, and this placard or a class 2.3 placard, must be displayed as of August 31, 2008. It may be displayed before that date.
Finally, a new subsection has been inserted to allow a placard to be displayed on tubes which are being used to transport goods of Class 2, Gases, and which are interconnected as a single unit and permanently mounted.
4.19(1)b) This paragraph has been changed to better describe which placards and UN numbers must be displayed at each end of a large means of containment.
4.22 The placard and UN number are not required to be displayed for substances identified as marine pollutants in subparagraph 2.43(b)(ii) when the marine pollutant mark is not required to be displayed in accordance with subsection (2) of 4.22.
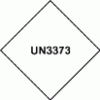
4.22.1 This new section introduces new requirements for displaying the Category B mark in the case of infectious substances included in BIOLOGICAL SUBSTANCE, CATEGORY B, UN3373.
Appendix The appendix to Part 4 has been changed through the addition of new safety marks for the following goods:
Class 2.3(8) gas
Infectious substances
Class 6.2
Class 7
Part 5 — Means of containment
The changes in this Part reflect changes in other Parts, regarding risk groups, the Explosives Vehicle Certificate (which will be abolished) and definitions. There are also changes concerning tank trucks. Other changes have been made as well.
5.1(3) The word “the” has been added after “accidental release of” to make the requirement more specific.
5.5 This section has been reworded.
5.7 The compatibility groups table has been changed to add the compatibility between groups B and S. New requirements are added for compatibility groups for mixed loads of explosives and new exemptions are introduced to exempt certain groups from table 5.7 requirements.
5.9 This section has been eliminated because it referred to the Explosives Vehicle Certificate (EVC), which is soon going to be abolished by Natural Resources Canada.
5.10(2)b) The date of manufacture of the means of containment has been removed.
5.10(3) This subsection has been reworded.
5.10(6) Tank trucks and certain portable tanks selected in accordance with CSA B622 manufactured and used in Canada after August 31, 2008 will have to be manufactured in accordance with CSA B620. They will also have to be tested and inspected in accordance with CSA B620 when the most recent periodic re-test or periodic inspection is performed in Canada on or after August 31, 2008.
5.11(1) The term “water capacity” is changed to “capacity” on the table in this section.
5.14 Tank trucks and certain portable tanks selected in accordance with CSA B621 manufactured and used in Canada after August 31, 2008 will have to be manufactured in accordance with CSA B620. They will also have to be tested and inspected in accordance with CSA B620 when the most recent periodic re-test or periodic inspection is performed in Canada on or after August 31, 2008.
Other changes have been made with regard to the standards that must be complied with.
5.16 References to risk groups have been removed, and the concept of Category A and Category B Infectious Substances has been added. The table in this section has been modified and defines new requirements to determine the appropriate means of containment.
5.16(1) Additional requirements for Type 1B means of containment are introduced.
Part 7 — Emergency Response Assistance Plan
In this Part, only section 7.1 has been changed. It now has 9 subsections, which give a better description of the ERAP requirements, in particular with regard to the accumulation of dangerous goods in means of containment.
7.1(1) This subsection no longer uses the term “consignment”; instead it speaks of a quantity of dangerous goods in a means of containment.
7.1(2) This subsection, dealing with an accumulation of dangerous goods, now refers to all means of containment, not just large means of containment. Only quantities in means of containment (being used to transport dangerous goods having the same UN number) whose individual capacity is greater than 10% of the limit in column 7 of Schedule 1 will be counted when determining whether an ERAP is required.
7.1(3) This subsection has been changed to make clear that it applies when goods are being transported in one or more means of containment. Also, paragraph a) has been changed to state how to calculate the net explosives quantity in terms of the number of articles and vice versa.
7.1(4) This subsection has been changed to better identify the point at which a quantity of dangerous goods requires an ERAP. The way of calculating the quantity is changed for gases and explosives. At least one of the means of containment transporting gases will have to have a capacity of over 100 L. For explosives, the question of whether Special Provision 86 applies must be taken into consideration.
7.1(5) A new subsection under which certain flammable liquids (UN1202, UN1203 et UN1863) will need an ERAP when transported in a train that has 34 tank cars, at least two of which are interconnected, and which are on average 70% full.
7.1(6) A new subsection requiring an ERAP for certain Class 6.2 Infectious Substances.
7.1(7) This subsection contains new requirements about authorization to use another person's ERAP. This may be done only if:
- the dangerous goods originate outside Canada and are being transported through Canada to a destination outside Canada; or
- the dangerous goods are being returned to the manufacturer or producer.
7.1(8) As per the Act of the 1992, this subsection ensures that a person who offers for transport or imports dangerous goods remains responsible for their ERAP even if another person uses their ERAP.
7.1(9) Any substance that would require an ERAP when a classification is determined in accordance with Part 2, Classification, requires an ERAP when a classification from the ICAO Technical Instructions, the IMDG Code or the UN Recommendations is used as permitted under section 1.10 of the TDG Regulations.
Part 8 — Accidental Release and Imminent Accidental Release Report Requirements
8.1(1) There is a change in the values in the Quantity column of the table in section 8.1(1), for Class 1, Explosives and Class 6.2, Infectious Substances. These values are used to determine whether a report must be made in the event of an accidental release of dangerous goods.
8.1(5)h) The requirement to make an immediate report to CANUTEC now applies to dangerous goods of Class 1, Explosives, as well as Class 6.2, Infectious Substances.
Part 9 — Road
9.1(1)a)(iii) The term “shipping name” has been changed to “classification”.
9.1(1)c) New paragraph stating that as of August 31, 2008, the labels and placards displayed for dangerous goods included in Class 2.3 or Class 6.1 and being transported by road vehicle from the United States to Canada, or through Canada, are the labels and placards required in these Regulations for the dangerous goods. The labels and placards may be displayed before August 31, 2008.
9.1(2) This subsection has been changed so that dangerous goods which are exempt from displaying safety marks or from a packaging requirement by 49 CFR, where the exceptions are not permitted in Canada, will have to be transported in accordance with the TDG Regulations.
9.2(3) This subsection now clarifies the requirement of displaying placards in accordance with Part 4, Dangerous goods safety Marks, on a road vehicle or a means of containment visible from outside when dangerous goods are being transported on the vehicle to or from an aircraft, aerodrome or air cargo facility. The option of displaying placards in accordance with the IMDG Code is no longer permitted.
9.3(3) This subsection now clarifies the requirement of displaying placards on a road vehicle or a means of containment visible from outside when dangerous goods are being transported on the vehicle to or from a ship, port facility or marine terminal.
9.5 This is a new section that identifies the maximum explosives quantity that can be transported in a single vehicle. There are three different maximums, depending on the type of explosives. This requirement applies not just to transborder movements but to all road vehicle transportation.
Part 10 — Rail
10.1(1)a)(iii) The term “shipping name” has been changed to “classification”.
10.1(1)c) New paragraph stating that as of August 31, 2008, the labels and placards displayed for dangerous goods included in Class 2.3 or Class 6.1 and being transported by rail from the United States to Canada, or through Canada, are the labels and placards required in these Regulations for the dangerous goods. The labels and placards may be displayed before August 31, 2008.
10.1(2) This subsection has been changed so that dangerous goods which are exempt from displaying safety marks or from a packaging requirement by 49 CFR, where the exceptions are not permitted in Canada, will have to be transported in accordance with the TDG Regulations.
10.2(3) This subsection now clarifies the requirement of displaying placards in accordance with Part 4, Dangerous goods safety Marks, on a railway vehicle or a means of containment visible from outside a railway vehicle when dangerous goods are being transported on the vehicle to or from an aircraft, aerodrome or air cargo facility. The option of displaying placards in accordance with the IMDG Code is no longer permitted.
10.3(3) This subsection now clarifies the requirement of displaying placards on a railway vehicle or a means of containment visible from outside a railway vehicle when dangerous goods are being transported on the vehicle to or from a ship, port facility or marine terminal.
10.5 This section has been repealed in order to remove the prohibition on transporting by railway vehicle a tank truck that contains dangerous goods.
10.6 This section has been changed and the table has been replaced. New requirements on the location of placarded railway vehicles in a train have been added.
10.7(3) This subsection has been changed and a table has been added in order to better describe the requirements on coupling of railway vehicles.
10.7(4) This subsection has been changed to introduce new requirements regarding inspection of tank cars that have received a report. Several items must be inspected, such as the welds and the draft gear pocket.
10.7(5) This new subsection exempts railway vehicles equipped with a cushioning device from section 10.7, under certain conditions.
Part 11 — Marine
11.1(2)a) The wording has been changed to clarify who is affected by this section.
11.1(2)c)(iv) This subparagraph has been changed to include section 5.11, Aerosol Containers for Class 2, Gases, as a requirement that must be complied with.
11.1(3) In the French version of this subsection, the singular “contenant” has been replaced by the plural “contenants”; there is no change in the English version (“means of containment”).
Part 12 — Air
12.1(1)b)(ii) In this subparagraph, the term “Risk Groups” has been replaced by “Infectious Substances”, since risk groups no longer exist.
12.2b) The shipping document is no longer to have the IATA format, but it must still contain the information required by the ICAO Technical Instructions and it must still have, on the left and right margins, red hatchings that are oriented to the right or to the left.
12.4 This section is renumbered as subsection 12.4(1).
12.4(1)f) The wording has been changed to better describe this requirement.
12.4(2) This new subsection allows a peace officer, as defined in section 1 of the Canadian Aviation Security Regulations, or an in-flight security officer to transport a loaded firearm on board an aircraft. This subsection replaces section 1.47 of the Regulations, which has been eliminated.
12.6 This section has been changed to remove the expression “risk group”. It also removes certain infectious substances from the exception described in this section.
12.7 This section has been repealed.
12.9(1)c)(iii) A few marking and lablelling exceptions were included for means of containment transported by aircraft under the limited access provision.
12.9(2)b) The French shipping name has been changed to UN1203, ESSENCE.
12.9(3)a) The expression “water capacity” has been changed to “capacity”.
12.9(3)b)(i) The expression “water capacity” has been changed to “capacity”.
12.9(6) The expression “gross mass” has been changed to “total capacity”.
12.9(7) This subsection has been changed to add new requirements for handling, offering for transport or transporting internal combustion engines and vehicles on board an aircraft.
12.9(8)b) The expression “water capacity” has been changed to “capacity”.
12.9(8)c) Fire extinguishes will now have to be packaged in accordance with Packing Instruction 213 of Chapter 4, Class 2 – Gases, of Part 4, Packing Instructions, of the ICAO Technical Instructions, rather than Instruction 200.
12.9(10)b) The expression “water capacity” has been changed to “capacity”.
12.9(12)d) The wording has been changed to better describe this requirement. The expression “dangerous goods” has been changed to “the dangerous goods”.
12.12(2)d) The wording has been changed to better describe this requirement. The expression “dangerous goods” has been changed to “the dangerous goods”.
12.14(2)a) The wording has been changed to better describe this requirement. The expression “dangerous goods” has been changed to “the dangerous goods”.
12.15 This section has been repealed. The exemption concerning air ambulances can now be found in section 1.48.
12.16 This section has been repealed. Some of the requirements pertaining to emergency response in the case of air transportation can now be found in section 1.26.
Part 16 — Inspectors
16.3 This new section contains new requirements pertaining to the detention of dangerous goods or means of containment. A copy of the Detention Notice has been inserted in the Regulations.
16.4 This new section contains new requirements pertaining to directions to remedy non-compliance. A copy of the Notice of Direction to Remedy Non-Compliance has been inserted in the Regulations.
16.5 This new section contains new requirements pertaining to directions not to import or to return to place of origin. A copy of the Direction Not To Import Or To Return To Place of Origin has been inserted in the Regulations.
Schedule 1 — Classes 1 to 9
The heading of column 4 has been changed to “Packing Group / Category” in order to replace the expression “risk group”, which no longer exists. The legends of columns 4 and 6-9 have been changed. Some of the information on a fair number of dangerous goods has been changed.
The class of ANHYDROUS AMMONIA, UN1005 has been changed to Class 2.3(8), Gases.
A new substance has been added to the list: ETHANOL AND GASOLINE MIXTURE, with more than 10 per cent ethanol, UN3475.
Schedule 2 — Special Provisions
This schedule has been changed by eliminating, changing or adding new special provisions. Some special provisions have been moved to Part 1, Coming into Force, Repeal, Interpretation, General Provisions and Special Cases of the Regulations.
SP 2 This special provision has been eliminated. It has been replaced by new requirements appearing in section 9.5, which sets limits on quantities of explosives that can be transported on a highway vehicle.
SP 4 to 9 These special provisions have been eliminated because Natural Resources Canada will soon be abolishing the Explosives Vehicle Certificate.
The new special provisions 4 and 5 describe how to calculate the net explosives quantity for certain dangerous goods of Class 1, Explosives, when the true quantity cannot reasonably be determined.
SP 29 This special provision concerning the shipping name, LIQUEFIED PETROLEUM GASES, UN1075, has been moved to section 1.32.1 and changed slightly. See the wording of section 1.32.1 for further detail.
SP 32 The wording of paragraph b) has been changed to clarify this exemption. The exemption as such has not been changed.
SP 42 This special provision concerning a partial exemption for certain gases of Class 2 has been moved to section 1.32.3 and changed slightly. See the wording of section 1.32.3 for further detail.
SP 75 This exemption has been eliminated.
SP76 This special provision replaces special provisions 76 and 77. It allows certain explosives to be transported together by road vehicle despite section 5.7.
SP 81 This is a new special provision that exempts certain dangerous goods included in Class 9 from complying with the requirements of section 5.12 concerning standardized small standard means of containment.
SP 82 This new special provision sets out the dangerous goods of Class 3 (UN1202, UN1203 and UN 1863) which require an ERAP in accordance with section 7.1(5) when they are transported on interconnected tank cars.
SP 83 This new special provision exempts certain flammable liquids of Class 3 (glues, inks, paints and resins) from the provisions of section 5.12 concerning standardized small means of containment, provided certain requirements are complied with.
SP 84 This new provision sets out the dangerous goods of Class 6.2 (UN2814 UN2900) which require an ERAP in accordance with subsection 7.1(6).
SP 85 Despite the index number in column 6 of Schedule 1, these dangerous goods may be handled, offered for transport or transported in accordance with section 1.31 of Part 1, Coming into Force, Repeal, Interpretation, General Provisions and Special Cases, when they are in a quantity that is less than or equal to 15 000 articles.
SP 86 Despite the index number in column 6 of Schedule 1, these dangerous goods may be handled, offered for transport or transported in accordance with section 1.31 of Part 1, Coming into Force, Repeal, Interpretation, General Provisions and Special Cases, when they are in a quantity that is less than or equal to 100 articles.
SP 87 This is an exemption for OXYGEN, REFRIGERATED LIQUID, UN1073 transported on a passenger carrying road vehicle or passenger carrying railway vehicle when it is used for medical purposes during transport and is in a means of containment with a capacity less than or equal to 1 L.
SP 88 This is a new special provision allowing the transportation of certain dangerous goods (UN1202, UN1203 and UN1978) in a passenger carrying road vehicle if the passengers on board are not being transported for hire or reward.
SP 89 This is a new special provision that will replace the permit for equivalent level of safety with respect to the transportation of tar in small means of containment.
Schedule 3 — Alphabetical Index
Some changes have been made, notably the addition of ETHANOL AND GASOLINE MIXTURE with more than 10 per cent ethanol, UN3475.
The following document is available for downloading or viewing:
To access the Word document (DOC) version you must have a DOC reader installed. If you do not already have such a reader, there are numerous DOC readers available for free download or for purchase on the Internet: