Follow these steps to find out which dangerous goods in your consignment need an emergency response assistance plan (ERAP).
Step 1: Before you start
Section 7.2 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations (TDG Regulations) provides the conditions and quantities above which an ERAP is required for each dangerous goods in your consignment.
Useful information
Before you can determine if you need an ERAP, find out:
- what dangerous goods are in your consignment
- the quantity of each dangerous goods
- the means of containment for each dangerous goods
- the mode of transport you will be using
The quantity is expressed in kilograms for solids, in litres for liquids, and, for gases, as the capacity in litres of the means of containment. For Class 1, Explosives, the quantity is expressed either in kilograms of net explosives quantity or, if the explosives are subject to special provision 85 or 86, number of articles.
A large means of containment has a capacity greater than 450 L whereas a small means of containment has a capacity less than or equal to 450 L.
Step 2: Find the information in Schedule 1 for each dangerous goods
Go to Schedule 1 of the TDG Regulations and search for the UN number or shipping name for one of dangerous goods to be transported. Some dangerous goods have more than one shipping name or packing group (PG) or category. Make sure you look at the right one.
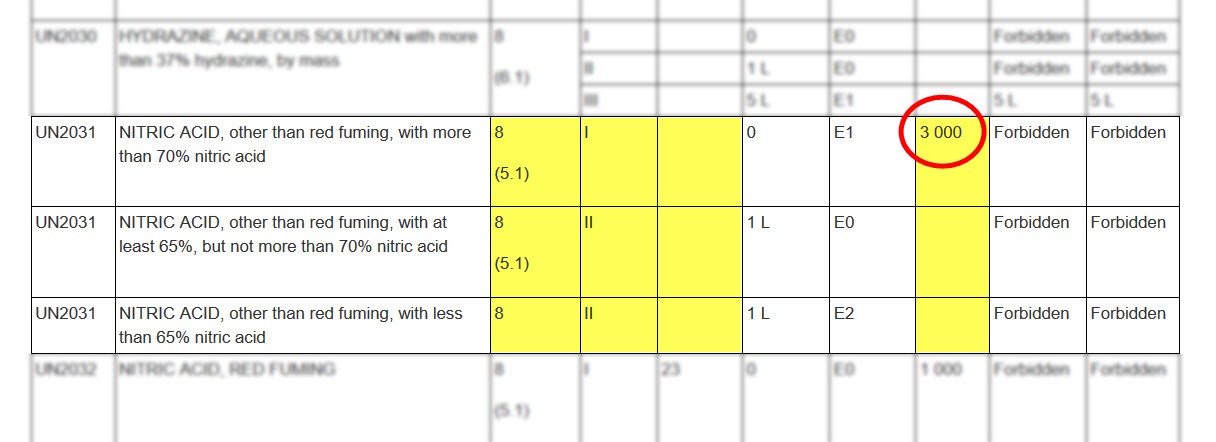
In this example, all three dangerous goods have the same UN number but have different shipping names. Only one has an ERAP index, circled in red.
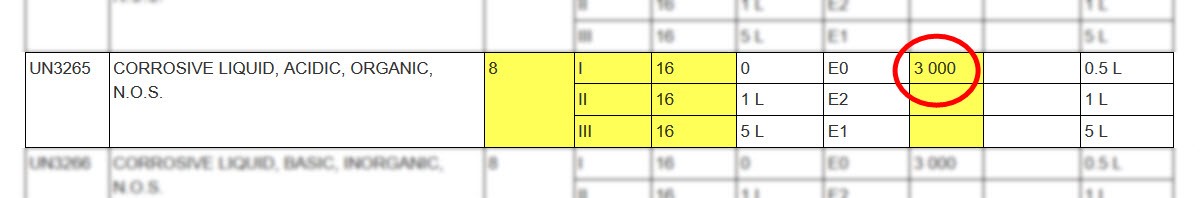
In this example, the UN number and the shipping name is the same but there are 3 packing groups. Only one has an ERAP index.
The information you will need for the next steps is in:
- Col. 3 Class
- Col. 4 Packing Group/Category
- Col. 5 Special Provisions
- Col. 7 ERAP Index
Find this information for all the dangerous goods in your consignment.
If one of your dangerous goods is not listed in Schedule 1, you must determine its classification according to Part 2 of the TDG Regulations. Subsection 2.2(4) of the TDG Regulations allows for substances to be classified using the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Technical Instructions, the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code or the United Nations (UN) Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods – Model Regulations. Using another set of regulations allowed under subsection 2.2(4) does not exempt you from ERAP requirements. As a result, any substance that would require an ERAP if its classification were determined in accordance with Part 2 requires an approved ERAP.
Step 3: Take the questionnaire
Answer the following questions for only one of your dangerous goods at a time.