- 12. Warning System Operation - General
- 13. Number and Location of Light Units
- 14. Light Units - Alignment
- 15. Bells and Gates
- 16. Circuitry
- 17. Warning Systems and Traffic Signals Installed at a Grade Crossing in Lieu of a Warning System - Inspection and Testing
12. Warning System Operation - General
12.0 Except as otherwise specified in articles 12 to 16 and Appendix B of these Standards or in the Grade Crossings Regulations, warning systems must be in accordance with the requirements and recommended practices of Part 3 of the AREMA Communications and Signals Manual (cited in Part A).
12.01 For the purposes of these Standards, the following interpretations and adjustments apply with respect to AREMA:
- Any guidelines, recommendations, and similar matters are to be considered mandatory;
- Any references to "should" are to be read as "must";
- The term "highway-rail grade crossing warning system" is to be read as "warning system";
- The term "railroad" and the phrase "operators of the passenger or commuter rail system" is to be read as "railway company";
- The term "lights" is to be read as "light units";
- The term "train" is to be read as "railway equipment";
- The term "roadway" and "roadway approach" is to be read as "road approach";
- All references to the "MUTCD" are to be disregarded;
- All "Purpose" articles, paragraph 2 of article 3.1.16 G.1.(b)(ii) and article 3.2.35 K 5, are to be disregarded;
- The following are to be disregarded:
- all references to and requirements related to the "Diagnostic Team";
- all references to and requirements related to the "highway agency" or "highway agency or authority with jurisdiction";
- all references to and requirements related to the "agency" or "public agency";
- all references to and requirements related to "manufacturers" except where the requirement is to do something in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions;
- all references to "unless otherwise specified" or "other considerations", all references to approvals or orders, and any other reference to the exercise of discretion;
- all purchase order requirements;
- all requirements to create or keep records;
- all requirements for a diagnostic review, an engineering study, a study of train operations, a risk analysis, a safety analysis, and all requirements to provide special instructions, operating rules, orders, or operational procedures.
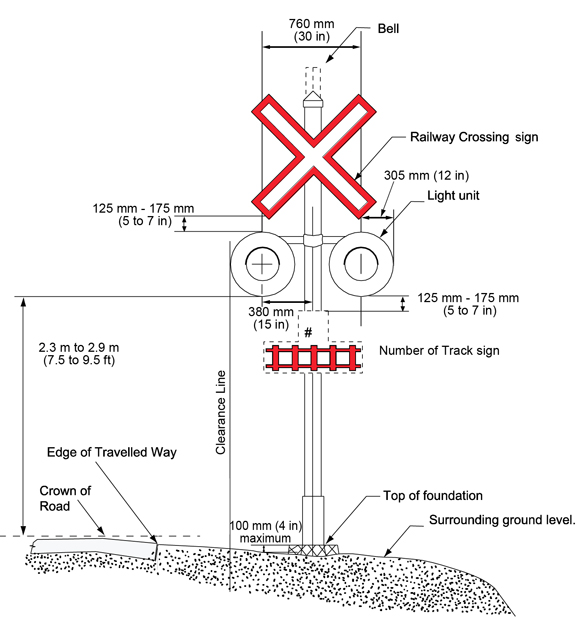
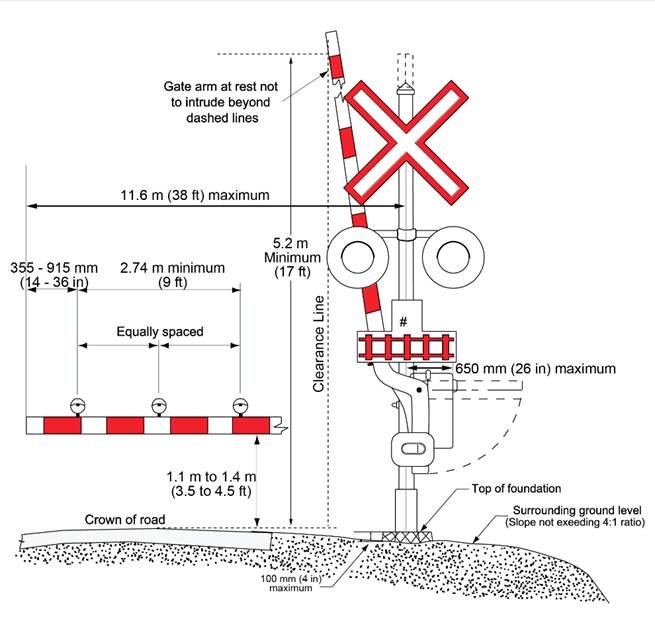
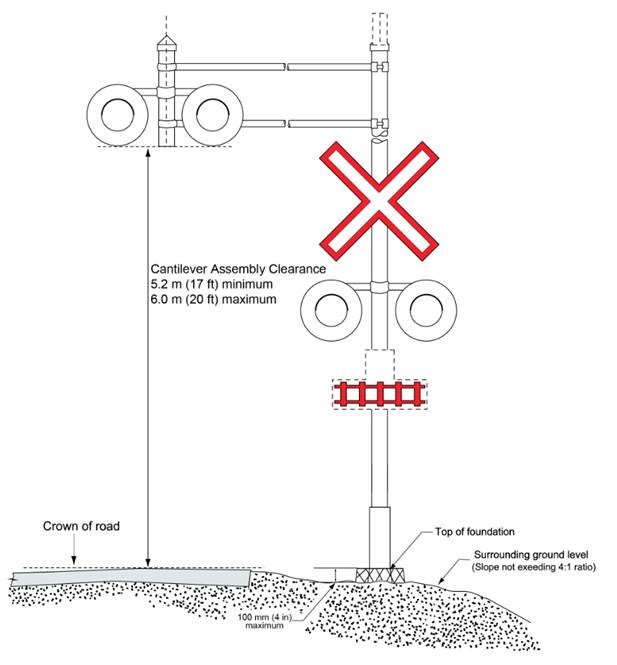
12.1 Signal assemblies must be as shown in Figure 12-1, and gate assemblies must be as shown in Figure 12-2 and the cantilever assembly's clearance must be as shown in Figure 12-3, and must meet the following specifications:
- The minimum clearance distance from the face of a curb to the clearance line must be 625 mm (2 ft);
- Where there is no curb, the minimum clearance distance must be 1.875 m (6ft) from the edge of the travelled way to the clearance line and a minimum of 625 mm (2 ft) from the outer edge of the road approach shoulder to the clearance line, if there is a shoulder;
-
The top of the warning signal foundation must be at a maximum of 100 mm (4 inches) above the surrounding ground. The slope of the surrounding ground away from the foundation toward the travelled way must not exceed the ratio of 4:1;
- The gate arm reflective materials shall have:
- stripes of 406 mm (16 inches), and must be affixed with white and red alternately and be aligned vertically;
- Retroreflective material must meet the specifications for Type XI, white sheeting, in sections 4 and 6 of ASTM D4956 (cited in Part A), when tested in accordance with the Test Methods for Type XI specified in sections 7 and 9 of that Standard; and
- The retroreflection coefficient of the retroreflective material referred to in (ii) is to be maintained above 50 per cent of the value specified for Type XI, white sheeting, in sections 4 and 6 of ASTM D4956 (cited in Part A).
- For grade crossings used by vehicles, gate arms must extend to within 1 m (3 ft) of the farthest edge of that portion of the road approach. Where gates are installed on each side of the same road approach, gate ends must extend to within 1 m (3 ft) of each other.
- Where gates are installed at sidewalks, paths or trails:
- Each gate arm must extend across the full width of the sidewalk, path or trail; and
- in the case of a sidewalk, path or trail that is less than 3.5 m (11.5 ft.) wide, two lights are required on each gate arm located so that the lights are over the two points dividing the sidewalk, path or trail into thirds. The two gate arm lights must flash alternately.
- the height of the cantilever assembly clearance must be between 5.2 m (17 ft) and 6.0 m (20ft) above the crown of the road as shown in Figure 12-3.
12.2 In addition, warning systems must have monitoring devices that gather and retain the date and time of the following information for a minimum of 30 days;
- Activation and deactivation of Interconnected devices;
- Gates have returned to or left the vertical position (Gate up Position);
- Gates have descended to a point 10 degrees from horizontal (Gate down Position);
- Activation of the warning system test switch
- Activation and deactivation of all track circuits used in the control of the warning system, including electronic track circuits;
- Activation of the warning system;
- Activation and deactivation of all devices used to control the warning systems at adjacent crossings; and
- Activation and deactivation of all devices used to activate the warning system from a location other than the crossing.
12.3 All control circuits that affect the safe operation of a warning system must operate in a manner that activates the warning system if there is a failure of a safety-critical component of that system.
12.4 The electromagnetic, electronic, or electrical apparatus of a warning system must be operated and maintained in accordance with the limits to which the system is designed to operate.
12.5 Railway track circuits must:
- detect railway equipment in any part of the track circuit;
- detect a shunt of 0.06 ohm resistance when the shunt is connected across the track rails of any part of the circuit;
- provide a set of fouling wires that consist of at least two discrete conductors and must ensure proper operation of the track circuit when the circuit is shunted. Single duplex wire with single plug is not permitted;
- in the case of a non-insulated rail joint within the limits of a track circuit, be bonded by means other than joint bars and the bonds must ensure electrical conductivity; and
- in the case of an insulated rail joint used to separate track circuits, prevent current from flowing between rails separated by the insulation.
12.6 Warning system battery back-up of 8 hours of continuous activation and 24 hours of normal railway operations must be provided.
Figure 12-1 - Text version
Lines and arrows are used to illustrate the dimensions of a warning signal assembly and the placement of the number of tracks sign.
The lowest edge of the light units, of the Warning Signal Assemblies, is to be located between 2.3 m and 2.9 m from the crown of the road. The outside radius of the light units is 305 mm. Each flashing light unit shall be located on each side of the mast and their center shall be at 380 mm from the center line of the mast.
The distance between the lowest edge of the railway crossing sign and the outer edge of the light unit is between 125 and 175 mm.
The distance between the top of the assembly foundation and the surrounding ground level is 100 mm.
Figure 12-2 - Text version
Lines and arrows are used to illustrate the dimensions of a warning signal assembly with gates and the placement of the number of tracks sign.
The gate arm is between 1.1 and 1.4 m above the crown of the road. The gate arm gearbox extends no more than 650 mm from the center of the mast. The gate arm at its fully deployed position is 11.6 m from the center of the mast.
The gate arm shall have 3 flashing lights positioned just above the gate arm and shall be equally spaced along the arm. The first light shall be located between 355 and 915 mm from the end of the gate arm. The distance between the first and last light shall be 2.74 m minimum.
Figure 12-3 - Text version
Lines and arrows are used to illustrate the dimensions of a warning signal assembly with lights mounted on cantilevers.
The outer edge of the cantilevered flashing light units is between 5.2 and 6.0 m from the crown of the road.
13. Number and Location of Light Units
13.0 Where incandescent lights are installed, the light unit voltage must be maintained between 90 and 110 per cent of the rated voltage under standby power conditions.
13.1 Light units must be installed in a warning system and located to ensure that the crossing user, on a road approach, or accessing a road approach:
- is within the effective distribution pattern of luminous intensity of a set of light units within the distances specified for the front light units within SSD; and
- is able to see at least one set of front light units clearly.
13.2 Except for when the visibility of units is obstructed by railway equipment, light units must be provided in a warning system and located to ensure that a crossing user in the stopped position at the grade crossing;
- is within the effective distribution pattern of luminous intensity of a set of back lights;
- so that at least one set of back lights is clearly visible to crossing users in each lane.
13.3 Cantilevered Light Units
13.3.1 Except on a one-way road where a second warning signal is installed on the left side of the lane, a cantilevered light unit must be provided in a warning system if:
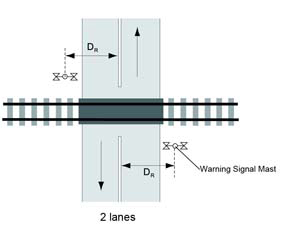
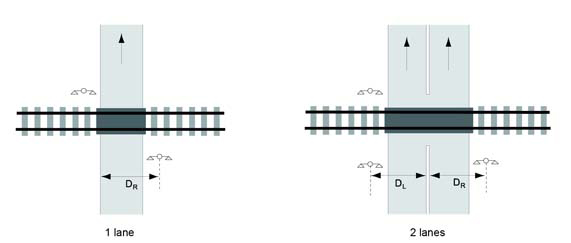
- the distance between the centre of a warning signal mast and the edge of the lane of the road that is the farthest from the mast, measured perpendicular to the road, exceeds 7.7 m for DR, and 8.7 m for DL as shown in Figure 13-1;
- the front light units of the warning signal (i.e. those on the same side of the track as approaching traffic) are not clearly visible within the distance for the set of light units as specified in article 14.4.
13.3.2 Cantilevered light units must be installed for a warning system on a road that meets the specifications for an expressway as specified in Table 10-4.
13.4 Light Units for a Sidewalk, Path or Trail
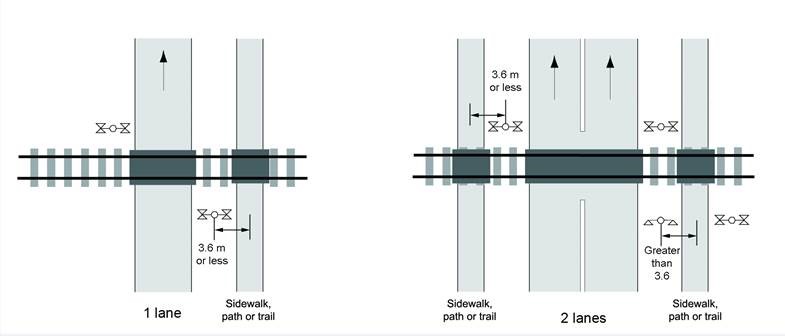
13.4.1 A sidewalk, path or trail with a centre line more than 3.6 m (12 feet) from the centre of a warning signal mast must have separate light units for each direction of travel, as shown in Figure 13-2(a).
13.4.2 Lights must be installed for persons travelling in the direction opposite to vehicle traffic where there is a sidewalk, path or trail along a one-way road as shown in Figure 13-2(b).
(a) Two-Way Road
Figure 13-1 (a) - Text version
Plan view of a grade crossing with dimensions and arrows to illustrate warning signal offset for a two-lane road.
In a two-way road configuration, Dr is the distance between the center of the warning signal mast and the centerline of the roadway.
Figure 13-1 (b) - Text version
Figure (b) has two diagrams of plan views of a grade crossing with dimensions and arrows to illustrate warning signal offset on a road. Diagram 1 is for a one way and diagram 2 is for a divided road approach.
In a one-way road configuration, DR is the distance between the center of the warning signal mast and the outer edge of the roadway on the opposite side of the warning system.
In a divided road configuration, DR is the distance take to the right of the plan view of the roadway, between the center of the warning signal mast and the centerline of the roadway. DL is the distance take to the left of the plan view of the roadway, between the center of the warning signal mast and the centerline of the roadway.
a) Two Way
Figure 13-2 (a) - Text version
A plan view of a grade crossing with dimensions and arrows illustrates the proximity of a sidewalk, path or trail and the location of light units.
As provided for in article 13.5.1, a sidewalk, path or trail with a centre line more than 3.6 m from a warning signal mast beside the travelled way of a road approach for vehicles must have separate light units
Figure 13-2 b) - Text version
Figure (b) has 2 diagrams of plan views of a grade crossing that illustrate the proximity of sidewalks and the location of light units. Diagram 1 is for a one-lane road with one sidewalk and diagram 2 is for a two-lane road with sidewalks on both sides.
As provided for in 13.5.2, a set of back lights must be provided for persons travelling in the direction opposite to vehicle traffic where there is a sidewalk, paths or trail along one-way road approach.
14. Light Units - Alignment
14.1 General – Light Units
14.1.1 Light units must be 200 mm or 300 mm Light Emitting Diode (LED) signal module type and as specified in Appendix A.
14.1.2 Sets of light units of warning systems must flash alternately and uniformly at a rate of 45 to 65 flashes per minute.
14.2 Alignment Height – Front and Back Lights for Vehicles
14.2.1 Light units must be aligned so that the axis of the light units pass through a point 1.6 m above the road surface at stopping sight distance.
14.3 Alignment Distance – Front Light Units for Vehicles
14.3.1 Front light units must be aligned through the centre of the approaching traffic lane for which they are intended as follows:
- at a minimum to the stopping sight distance; or
- at the point at which the light units are first visible, if this point is less than the distance specified in (a).
14.4 Alignment – Intermediate Front Light Units for Vehicles
14.4.1 Additional sets of light units must be aligned to cover any intermediate areas of the road approaches between the coverage provided by the front light units aligned as required in article 14.3 and the back lights aligned as required in article 14.5.
14.4.2 Additional sets of light units provided for crossing user must be aligned through the point that is 1.6 m above ths surface of the road at the point at which the crossing user enters the road approach.
14.5 Alignment – Back Light Units for Vehicles
14.5.1 Back light units intended for motor vehicles approaching the grade crossing from a lane on the opposite side of the line of railway from the warning signal on which they are installed, must be aligned through the centre of that lane, 15 m in advance of the warning signal for that side of the line of railway.
14.6 Alignment – Light Units Installed Exclusively for Sidewalks, Paths or Trails
14.6.1 Light units installed exclusively for sidewalks, paths, or trails, must be aligned to be visible through a point 1.6 m above the centre of the sidewalk, path or trail and 30 m (100 ft) in advance of the nearest rail on both sides of the line of railway or the point at which the set of lights units first become visible if less than 30 m (100 ft).
15. Bells and Gates
15.1 Bells
15.1.1 A bell is required for all warning systems, except for limited use warning systems referred to in Appendix B and for limited use warning systems with walk lights referred to in Appendix C.
15.1.2 Where there is only one sidewalk, path or trail along a road approach, the bell must be located on the signal mast adjacent to the sidewalk, path or trail.
15.1.3 A bell is required on a signal mast adjacent to a sidewalk, path or trail if separated from any other signal mast with a bell by more than 30 m (100 ft).
15.1.4 All bells must continue to operate for the same duration as the light units.
15.2 Gates
15.2.1 The gate arm must be installed perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the road approach.
15.2.2 The descent of the gate arm must take 10 to 15 seconds and its ascent must take 6 to 12 seconds.
15.2.3 The gate arm must begin its decent once the gate arm clearance time has elapsed, calculated in accordance with article 10.4.
15.2.4 For a grade crossing where railway equipment enters the grade crossing at more than 25 km/h (15 mph), the gate arm must rest in the horizontal position not less than 5 seconds before the arrival at the crossing surface of railway equipment.
15.2.4.1 For a grade crossing where the railway equipment enters the grade crossing at 25 km/h (15 mph) or less, the gate arm must rest in the horizontal position when the railway equipment arrives at the crossing surface.
15.2.5 The gate arms must operate uniformly, smoothly, and complete all movements without rebound, and must be securely held when in the raised position.
15.2.6 If the gate arm strikes or fouls any object during its ascent or descent, it must readily stop and, on removal of an obstruction, assume the position corresponding with the control apparatus.
16. Circuitry
16.1 Warning Time
16.1.1 The time during which the warning system must operate, before the arrival of railway equipment at the crossing surface, must be the greatest of:
- 20 seconds, unless the grade crossing clearance distance (Figure 10-1) is more than 11 m (35 ft), in which case, the 20 seconds must be increased by one second for each additional 3 m (10 ft), or fraction thereof;
- the Departure Time for the design vehicle (article 10.3.2);
- the Departure Time for pedestrians, cyclists, and persons using assistive devices (article 10.3.3);
- the gate arm clearance time, plus the time to complete the gate arm descent, plus 5 seconds;
- the minimum warning time required for traffic signal interconnection as referred to in article 19.3(a);
- the time for the design vehicle to travel from the stopping sight distance, and pass completely through the clearance distance.
16.2 Consistency of Warning Times
16.2.1 Operating control circuits must provide consistent warning times for railway equipment regularly operating over the grade crossing.
16.2.2 Where the maximum railway operating speed has been reduced, the approach warning times for railway equipment regularly operating over the grade crossing, must not be more than 13 seconds longer than the warning time for the railway design speed.
16.3 Cut-Outs
16.3.1 Where railway equipment regularly stops, or railway equipment is left standing, within the activating limits of a warning system, the warning system must be equipped with a control feature to minimize the operation of the warning system.
16.3.2 A switch, when equipped with a switch circuit controller connected to the point and interconnected with the warning system circuitry, must cut out only when the switch point is within one-half inch of full reverse position.
16.4 Directional Stick Circuits
16.4.1 Where a warning system is equipped with directional stick circuits, the circuit must:
- include a stick release timer to activate the warning system after a preset time if there is failure of an approach circuit; or
- cause a train control signal system to restrict railway equipment speed to 25 km/h (15 mph) or less.
16.5 Identification
16.5.1 Each wire in all housings, including switch circuit controllers and terminal or junction boxes, must be identified at each terminal and the identification must not interfere with moving parts of the warning system. Material used for identification purposes must be made of insulating material. This requirement does not apply to light units or wiring that is an integral part of solid state equipment.
17. Warning Systems and Traffic Signals Installed at a Grade Crossing in Lieu of a Warning System - Inspection and Testing
17.1 Inspection and testing of warning systems must be done in accordance with article 3.3.1 and 3.1.15 of AREMA Communications and Signals Manual (cited in Part A).
17.2 Inspection and testing of traffic signals installed at a grade crossing in lieu of a warning system must be done in accordance with the road authority's procedures.
Table 17-1 – Interpretation of Frequencies of Inspections and Tests for Warning Systems and Traffic Signals installed at a grade crossing in lieu of a warning system
| Designated Frequency | Definition | Maximum interval between each inspection or test |
|---|---|---|
| Weekly |
Once every week (Sunday to Saturday) |
10 clear days |
| Monthly | Once every calendar month | 40 clear days |
| Quarterly |
Once every 3 months (January to March, April to June, July to September, and October to December) |
100 clear days |
| Twice annually |
Once every 6 months (January to June and July to December) |
200 clear days |
| Annually | Once every calendar year | 13 months |
| Every 2 years | Once every 2 calendar years | 26 months |
| Every 4 years | Once every 4 calendar years | 52 months |
| Every 10 years | Once every 10 calendar years | 130 months |
Table 17-2 – Required Frequencies of Inspections and Tests for Warning Systems and Traffic Signals installed at a grade crossing in lieu of a warning system
| ITEM | Elements: Inspection and Testing requirements | Frequency for Warning Systems Systems and Traffic Signals installed at a grade crossing in lieu of a warning system | Frequency for Limited Use Warning Systems | Frequency for Limited Use Warning Systems with Walk Light |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Warning Systems: for operation of lights, bell, gates, and power off light. | Weekly or no more than 7 days before the operation of railway equipment | N/A | N/A |
| 2 | Light units: for misalignment, physical damage and conspicuity. | Monthly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 3 | Standby power: for operating bank voltage | Monthly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 4 | Light units, and gates: for damage, cleanliness, and visibility | Monthly | Quarterly | N/A |
| 5 | Bell: for operation | Monthly | N/A | N/A |
| 6 | Gate arm: for operation | Monthly | N/A | N/A |
| 7 | Surge protection: for condition | Monthly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 8 | Circuits: for grounds | Monthly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 9 | Battery: for isolation faults | Monthly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 10 | Batteries: for voltage, current, electrolyte level, and plate deterioration where plates are visible | Monthly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 11 | Interconnection components: for energization of circuits as intended. | Monthly | N/A | N/A |
| 12 | Switch circuit controller: for adjustment | Quarterly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 13 | Batteries: for degree of exhaustion, voltage and current | Quarterly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 14 | Fouling circuits: for continuity | Quarterly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
| 15 | Direct Current relays: visual check of condition | Twice Annually | Twice Annually | Twice Annually |
| 16 | Bond wires, track connections, insulated joints, and other insulated track appliances: visual check of condition | Twice Annually | Twice Annually | Twice Annually |
| 17 | Cut-out circuits (any circuit that overrides the operation of a warning system): for operation | Twice Annually | Twice Annually | Twice Annually |
| 18 | Gate mechanism and circuit controller: visual inspection of condition | Twice Annually | N/A | N/A |
| 19 | Control circuits operation of traffic signals installed at a grade crossing in lieu of a warning system | Twice Annually | N/A | N/A |
| 20 | Light units: for proper alignment, focus, and visibility. | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 21 | Light Unit: for voltage | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 22 | Track circuits: for proper functioning | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 23 | Flash controller: for flash rate | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 24 | Battery: load test | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 25 | Warning time: for required time | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 26 | Electronic railway equipment detection devices, including processor-based systems: for programming and function ability. | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 27 | Timing relays and timing devices: for required time | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 28 | Cable and wire entrances: for condition | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 29 | Switch circuit controller centering device: for condition | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| 30 | Interconnection operation between of warning systems and traffic control devices | Annually | N/A | N/A |
| 31 | Pole line and attachments: for condition | Every Two Years | Every Two Years | Every Two Years |
| 32 | Gate mechanism: for electrical values, mechanical clearances and torque | Every Four Years | Every Four Years | Every Four Years |
| 33 | DC Polar, AC Vane, and Mechanical Timer relays: for electrical values and operating characteristics | Every Two Years | Every Two Years | Every Two Years |
| 34 | Relays that affect proper functioning of a warning system (except for DC polar, AC Vane and Mechanical Timer): for electrical values and operation | Every Four Years | Every Four Years | Every Four Years |
| 35 | Ground: for resistance value | Every Ten Years | Every Ten Years | Every Ten Years |
| 36 | Wire and cable insulation: for resistance | Every Ten Years | N/A | N/A |